It is hard to develop parts and devices for the medical industry. The reason is that the process can be complicated and the speed to reach the market and accuracy of the part is critical for its success. After evaluating product designs and selecting the materials, a production process that will allow flexibility is essential. This is where low volume manufacturing comes in. A supplier that can consistently, quickly and cost-effectively produce the parts is critical to its success.
Low volume manufacturing is done by selecting from an array of manufacturing methods. It will make sure that the production of medical devices and parts will smoothly move from prototyping to production.
Table of Contents
ToggleCustomize Low Volume Manufacturing
The medical industry demands for more customization and diversity than the rest. This demand esteems from advancement in medical science and a shorter life cycle of medical products. As such new product launch cycle shortens, more flexible innovations and time-to-market are all critical. Given the current market situation, the development of product designs are fast, and product developers shifted from mass production to low volume manufacturing.
The processing methods, materials used, mold tooling and processing methods, low volume production applies to the manufacture of parts with the range of 100 to 100,000. There are high cost and risks associated with mass production. Low volume production, on the other hand, reduces the risk, provides flexibility on the designs, saves production costs, and reduces production time. This benefits the medical industry more due to the nature of requirements.
Benefits of Low Volume Manufacturing
There are many reasons why short runs or low volume manufacturing fits the medical industry more. Here are some of the advantages of low volume manufacturing and how it benefits this industry.
Flexible when it comes to product iterations
Choosing low product runs provides a more relaxed environment for designers and engineers to validate the design against the finished part. Before it is costly to change the design mid-production, but now they can do iterations after the pilot run to improve and optimize the product. The medical industry needs this type of flexibility because much is at stake on the part.
Short turnaround time means lower production cost
The costs of tooling and setting up are crucial components of the production budget. Low volume manufacturing is a more cost-effective method than mass production because it has shorter building and cycle time, reducing overall production cost.
Additionally, low volume production does not impose minimum order requirements because there is no substantial production investment to offset. This is beneficial for the medical industry as it requires a faster and more flexible quantity of products.
Serves as Interim Phase Between Prototyping and Production
Producing pre-production components is helpful before moving to final production. With pilot runs, the company can do their test on the form and function of the product. It will also allow issues to be discovered and corrected before going on mass production.
What to Look for in a Low Volume Manufacturer
The product development in the medical field has only one goal – to get FDA approval and therefore, you need a manufacturer who can provide quality parts. You need to select a manufacturer who has streamlined their process to remove inefficiencies.
The low volume manufacturer should also be able to accommodate many iterations on the product in a short time, especially in injection molding. Aside from the quick turnaround time, the manufacturer should also be able to provide fast quoting to get the parts in a few hours.
It should be able to provide immediate design feedback to improve the manufacturability of the product. This will help to accelerate the process and will result in a better product.
Some Manufacturing Methods for Low Volume Production
Additive Manufacturing
It is sometimes called 3D printing and is an excellent method to use when you need to evaluate a new product design that has complex geometries quickly. It is low cost compared to the cost of tooling, and it is easy to make design changes. The downside of this manufacturing method is it has higher per piece cost, offers limited texture and colors. Medical device developer used 3D printing to identify the design flaws and make changes.
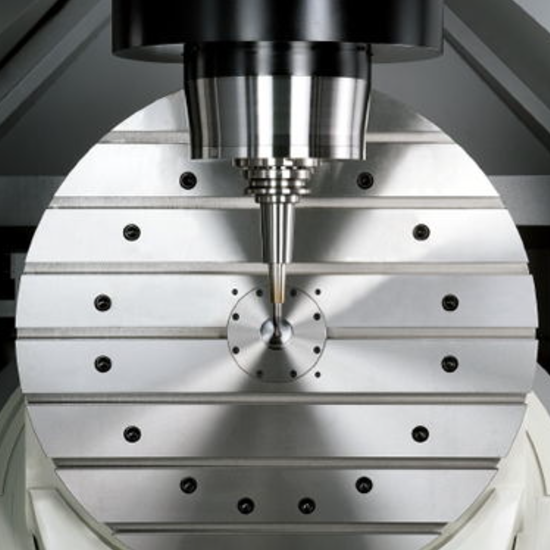
CNC Machining
The process is opposite to additive manufacturing, as it starts with a block of material. A tool begins on removing the material to create the part. It is often used in the early and end of the products life cycle. Machining allows the developer of medical devices to test the part design in parallel. This shortens the developmental cycle and allows perfecting the product to pass through the FDA. It is also essential in testing devices and parts that use engineering-grade materials. At the end of the device’s life, CNC machining is cost-effective in providing parts no longer available in the market.
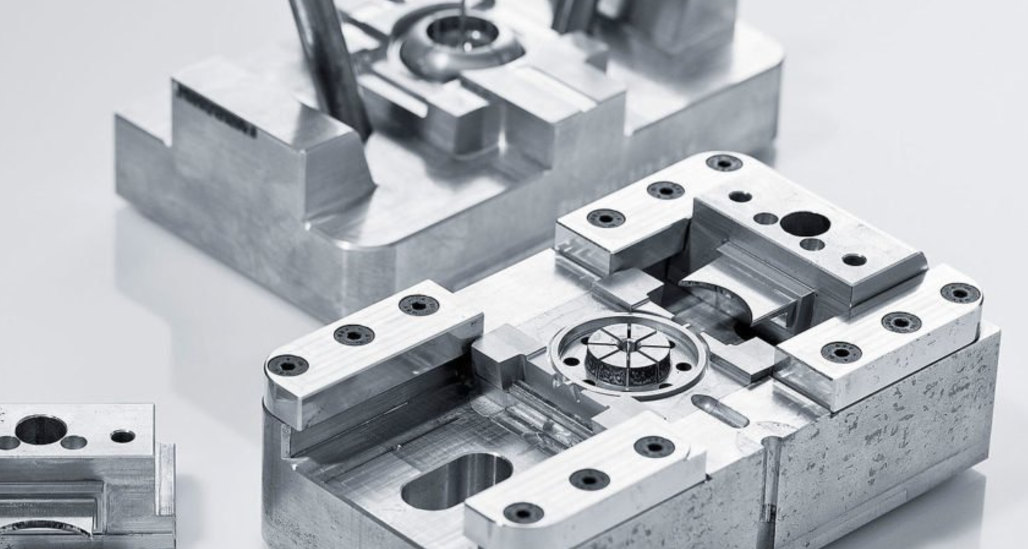
Injection Molding
This method is the most common in developing parts and devices and can produce parts from metal, plastic, or silicone rubber. The process can also provide repeatable, consistent, and reliable results. The downside of injection molding in low volumes is the high upfront cost because of the price of tooling per part and the risk of design changes after tooling that can be costly.
Conclusion
Low volume manufacturing is vital for the medical industry because finding a prototyping supplier that can perform short runs is critical to the success of a part or product. By knowing the product flaws fast and learning what doesn’t work, companies can do reiterations quickly, which is essential in passing the FDA.